Parameters Of Car Wheels
Have you ever thought about this question when considering replacing your wheels: What kind of wheels are suitable for my car, or what specifications must the wheels have to be installed on my car?
When purchasing wheels, there are four main factors to consider to ensure they fit your car. These are the bolt pattern or Pitch Circle Diameter (PCD), wheel offset, wheel width, and whether the car can use a square or staggered setup. Lastly, the car's hub bore and the wheel's center bore must be considered. All the wheels we suggest or recommend for your car are guaranteed to fit perfectly and provide a vibration-free ride. If any issues arise due to our wheels, we offer a full refund. These parameters may sound complicated, but we will explain them to you one by one.
Bolt Patterns or Pitch Circle Diameter (PCD)s
BOLT PATTERNS OR PITCH CIRCLE DIAMETER (PCD)
When it comes to finding the proper fitment for putting aftermarket or other new wheels on your car, the bolt pattern is possibly the most important consideration. There is a perfectly obvious reason for this,since “bolt pattern” refers to the number of lug holes in the wheel and the distance between them. The bolt pattern on the wheel must match the bolt pattern on the vehicle they are being fitted to, or the wheel will not fit. All BMW cars in the current line up have a bolt pattern of 5 holes x 112/120mm or abbreviated to 5 x 112/120. All Porsche cars have 5 holes x 130mm or 5 x 130. This means that BMW wheels will not fit on the wheel hubs of any Porsche.
The bolt pattern is comprised of two numbers - the first indicates how many bolt holes are on the wheel, and the other describes how far apart they are. A bolt pattern of 5 x 115mm would mean the wheel has 5 bolt holes and they are 115mm apart (measured across the center of the wheel).
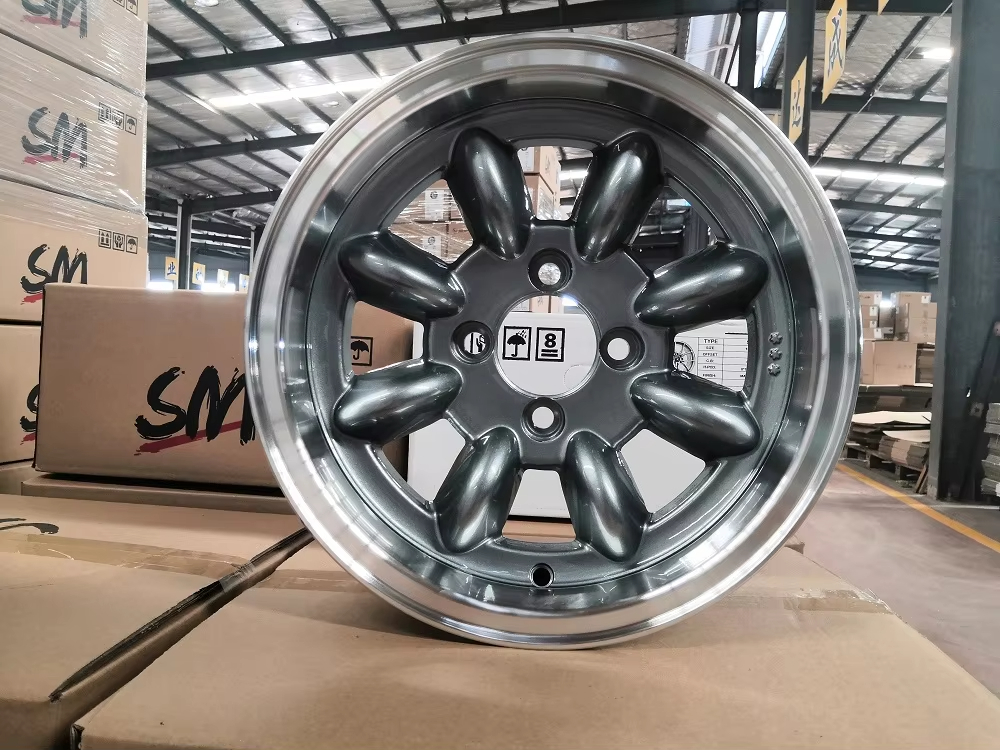
We sell wheels with 4, 5, 6, and 8 bolt applications:

4 Bolt Wheel
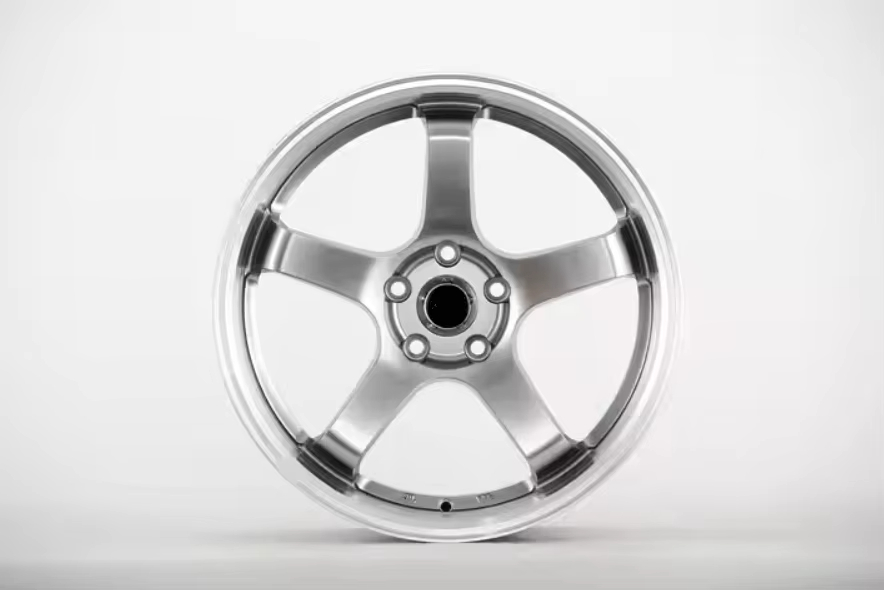

5 Bolt Wheel
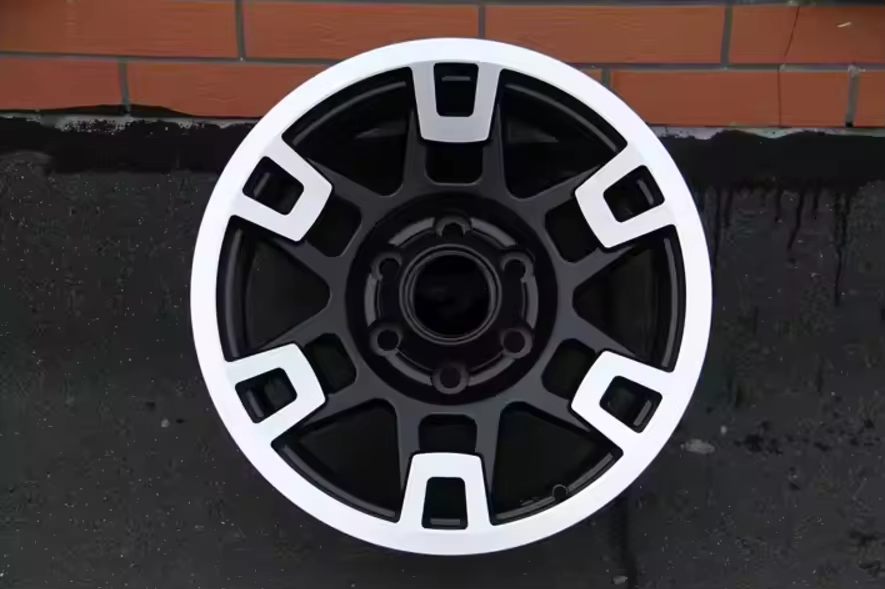

6 Bolt Wheel

8 Bolt Wheel
Dual bolt pattern or universal bolt pattern: More and more manufacturers are producing wheels with two bolt patterns. This increases the number of compatible fitments for the wheel. For example, a wheel with a bolt pattern of 4-100/114.3 has 8 bolt holes, allowing it to fit both 4 x 100mm and 4 x 114.3mm applications.

Measuring your Bolt Pattern
Measuring 4, 6, and 8 bolt patterns: They are measured from the center of one lug hole to the center of another hole.
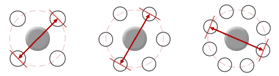
Examples of bolt pattern measurements.
Measuring a 5-bolt pattern: A 5-bolt pattern is very difficult to measure without using a bolt pattern gauge. Basically, you would measure the diameter of a circle that crosses through the center of the lug holes. This method is not recommended to confirm wheel fitment.
WHAT ARE WHEEL OFFSETS?
What is wheel offset? The offset of a wheel determines the position of the tire and wheel assembly relative to the suspension. More specifically, it is the measured distance between the wheel hub mounting surface and the centerline of the rim. Below is an explanation of the different types of offsets shown in the diagram above.
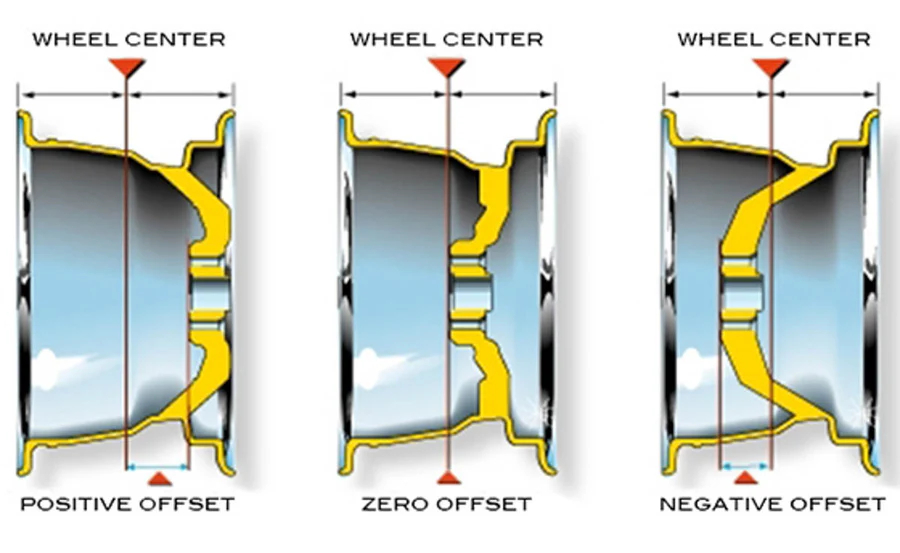
Positive Offset
A positive offset occurs when the hub mounting surface is on the street side (the side you see) of the wheel's centerline. Most factory wheels have this type of offset.
Zero Offset
When the hub mounting surface is at the center of the rim, it is called zero offset.
Negative Offset
If the hub mounting surface is on the brake side of the wheel's centerline, it is considered negative offset or "deep dish."
Please note that excessive negative offset may increase steering wheel kickback and put additional stress on the entire suspension system of the vehicle.
If you need more information about wheel offset, feel free to visit or call your nearest store.
HUB BORE & CENTER BORE
The center bore of a wheel is the size of the hole on the back of the wheel that allows it to sit centered on the car’s mounting hub. Some factory wheels have a center bore that perfectly matches the hub to keep the wheel centered and reduce vibrations. Wheels with a correctly sized center bore for the vehicle they are being mounted on are called hub-centric wheels. Hub-centric wheels relieve stress on the lug nuts, reducing their role in centering the wheel on the vehicle.
Non-hub-centric wheels are called lug-centric wheels because the centering is done by the lug nuts, provided they are properly tightened.
The center bore of aftermarket wheels must be equal to or larger than the vehicle’s hub center bore; otherwise, the wheel will not fit onto the vehicle. Many aftermarket wheels come with "hub-centric rings" that lock into or slide into the back of the wheel to adapt a larger center bore to a smaller hub. These adapters are usually made of plastic, but some are also made of aluminum. Plastic rings provide only initial centering and are not strong enough to help support the wheel when hitting potholes at high speed. Steel rings are the strongest, while aluminum rings offer moderate strength.






